What is spread in Forex Trading?
Spread is one of the most commonly used terms in the world of Forex Trading. The definition of the concept is quite simple. We have two prices in a currency pair. One of them is Bid price and the other is Ask price. Spread is the difference between the Bid (selling price) and the Ask (buying price).
With the business point of view, brokers have to make money against their services.
- The brokers make money by selling a currency to the traders for more than what they pay to buy it.
- The brokers also make money by buying a currency from the traders for less than what they pay to sell it.
- This difference is called spread.
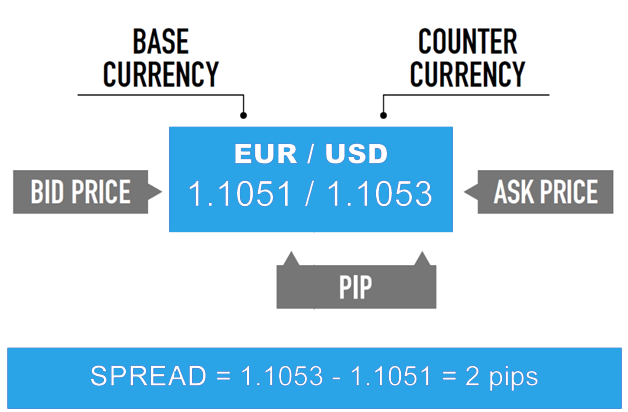
What does spread mean?
The spread is measured in terms of pips which is a small unit of price movement of a currency pair. It is equal to 0.0001 (fourth decimal point on quote price). This is true for most of the major pairs while Japanese Yen pairs have second decimal point as the pip (0.01).
When the spread is wide, it means the difference between “Bid” and “Ask” is high. Hence, the volatility will be high and liquidity will be low. On the other hand, lower spread means low volatility and high liquidity. Thus, the spread cost will be small when the trader trades a currency pair with tight spread.
Mostly currency pairs have no commission in trading. So spread is the only cost that traders have to bear. Most of the forex brokers do not charge commission; hence, they earn by increasing the spread. The size of spread depends on many factors like market volatility, broker type, currency pair, etc.
What does the spread depend on?
The spread indicator is usually presented in the form of curve on a graph that shows the direction the spread between the “Ask” and “Bid” prices. This can help the traders to visualize the spread of a currency pair over the time. The most liquid pairs have tight spreads while exotic pairs have wide spreads.
In the simple words, the spread depends on market liquidity of a given financial instrument i.e., the higher the turnover of a particular currency pair, the smaller the spread. For example, EUR/USD pair is the most traded pair; therefore, the spread in the EUR/USD pair is the lowest among all other pairs. Then there are other major pairs like USD/JPY, GBP/USD, AUD/USD, NZD/USD, USD/CAD, etc. In the case of exotic pairs, the spread is multiple times larger as compared to the major pairs and that’s all because of thin liquidity in exotic pairs.
Any short-term disruption to liquidity is reflected in the spread. This refers to situations like macroeconomic data releases, the hours when major exchanges in the world are closed, or during major bank holidays. The liquidity of instrument allows to determine whether the spread will be relatively large or small.
- Economic news
Market volatility may affect the spreads in forex. For example, the currency pairs may experience wild price movements at release of major economic news. Thus, the spreads are also affected at that time.
If you want to avoid a situation when spreads go too wide, then you should keep an eye on the forex news calendar. It will help you to stay informed and tackle the spreads. Like, non-farm payrolls data of the U.S. brings a high volatility in the market. Therefore, the traders can stay neutral at that time to mitigate the risk. However, unexpected news or data are hard to manage.
- Trading volume
Currencies with high trading volume have usually low spreads such as the USD pairs. These pairs have high liquidity but still these pairs have risk of widening spreads amid economic news.
- Trading sessions
Spreads are likely to remain low during the major market sessions like Sydney, New York and London sessions, particularly when the London and New York sessions overlap or when the London session ends. Spreads are also affected by general demand and supply of currencies. High demand of a currency will result in narrow spreads.
- Importance of broker's model
Spread is also dependent on business model of a broker.
- Market makers mostly provide fixed spreads.
- In the STP model, it can be a variable or fixed spread.
- In ECN model, we only have market spread.
All of these broker models have their own pros and cons.
What types of spreads are in Forex?
The spread can be fixed or variable. Like, indices have fixed spreads mostly. The spread for Forex pairs are variable. So, when the bid and ask prices change, the spread also changes.
1. Fixed spread
The spreads are set by the brokers and they do not change regardless of market conditions. The risk of a liquidity disruption is on broker’s side. However, the brokers keep high spread in this type.
Market maker or dealing desk brokers offer fixed spreads. Such brokers buy large positions from liquidity providers and then offer those positions in small portions to the retail traders. The brokers actually act as a counterparty to the trades of their clients. With the help of a dealing desk, the forex brokers are able to fix their spreads as they are able to control the prices that are displayed to their clients.
As the price comes from a single source, thus, the traders may frequently face problem of requotes. There are certain times when the prices of currency pairs change rapidly amid high volatility. Since the spreads remain unchanged, the broker will not be able to widen the spreads in order to adjust to the current market conditions. Therefore, if you try to buy or sell at specific price, the broker will not allow to place the order rather the broker will ask you to accept the requoted price.
The message of requote will be displayed on your trading screen to inform you that the price has moved and if you agree to accept the new price or not. It is mostly a price that is worse than your ordered price.
When prices move too fast, you may face the issue of slippage. The broker may not be able to maintain the fixed spreads and your entry price may be different than your intended price.
2. Variable Spread
In this type, spread comes from the market and the broker charges for its services on top of it. In this case, the broker has no risk because of liquidity disruption. The traders usually enjoy tight spreads except for volatile market movements.
Non-dealing desk brokers offer variable spreads. Such brokers get their price quotes of currency pairs from many liquidity providers and theses brokers pass the prices directly to the traders without any intervention of a dealing desk. It means that they have no control over the spreads and spreads will increase or decrease depending on overall volatility of the market and supply and demand of currencies.
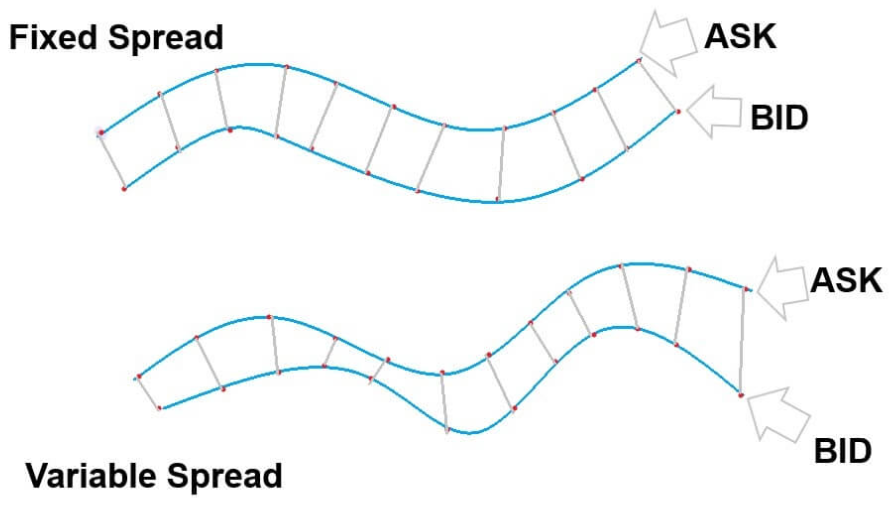
Comparison of fixed and variable spreads
Some of the advantages and disadvantages of fixed and variable spreads are discussed as below:
Some of the benefits and drawbacks of these two types of spreads are outlined below:
|
Fixed Spread
|
Variable Spread
|
|
May have requotes
|
Risk of requotes does not exist
|
|
Transaction cost is predictable
|
Transaction cost is not always predictable
|
|
Capital requirement is small
|
Capital requirement is relatively bigger.
|
|
Appropriate for beginners
|
Appropriate for advanced traders
|
|
Volatile market does not affect the spread
|
Spread may get widened at times of high volatility
|
How are spreads measured in Forex trading?
The spread is calculated within the price quote by last large number of ask and bid price. The last large numbers are 9 and 4 in the image below:
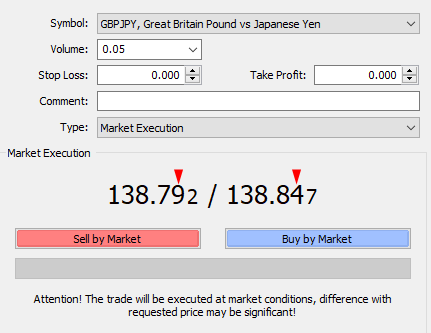
You have to pay the spread upfront whether you trade through CFD or spread betting account. This is the same as traders pay commission while trading shares CFDs. The traders are charged for both entry and exit of a trade. Tighter spreads are highly favorable for traders.
For example: The bid price for the GBP/JPY pair is 138.792 while the ask price is 138.847. If you subtract 138.847 from 138.792, you get 0.055.
As last large number of price quote is the base of spread; hence, the spread is equal to 5.5 pips.
What is relationship of margin with spread?
You may have a risk of receiving margin call if the forex spreads dramatically widen and the worst case is, positions being automatically liquidated. However, a margin call occurs only when the account value drops below the 100% margin requirement. If the account reaches below the 50% requirement, all of your positions will be automatically liquidated.
Summary
Forex spread is the difference between the ask price and the bid price of a Forex pair. Usually, it is measured in pips. It is important for traders to know what factors influence the variation in spreads. Major currencies have high trading volume; hence their spreads are low while exotic pairs have wide spread amid low liquidity.
Click on the button below to Download our "What is spread in Forex Trading" article in PDF




