How to build a trading plan and stick to it
A trading plan serves as a detailed document which defines the methods for identifying trades and their subsequent execution and management. The system functions as a navigation tool which enables traders to make rational trading choices and maintain stable performance during market fluctuations. Trades operate without a plan which results in unpredictable outcomes and uncontrolled risk exposure.
A trading plan exists to establish pre-defined rules which determine entry points for trades along with capital allocation and exit strategies. The system creates accountability which helps prevent hasty decisions based on temporary market price fluctuations. The trading strategy includes a 2% risk limit for each position to safeguard account equity from market price fluctuations.
A well-written plan also sets expectations. Traders who set profit targets and stop-loss levels create a system to track their performance while making adjustments to their strategies when actual results differ from their targets. A trading plan functions as a system for managing market results instead of market analysis.
Step 1 — Define objectives, constraints, and risk profile
The foundation of every trading plan requires traders to establish specific personal goals together with their risk tolerance limits. The goals of traders differ because some traders seek to earn extra profits on a regular basis yet others concentrate on building their wealth over time. The process requires to establish specific measurable targets which define success through return percentage achievements during predetermined time frames.
Constraints are equally important. The three essential elements which affect trading choices consist of account size and available trading hours and maximum drawdown tolerance. A trader who starts with $10,000 capital will establish their risk limit at $200 per trade because this amount equals 2% of their total account value. The basic principle functions as a protection mechanism which prevents the account from being drained quickly during multiple losing trades.
Risk tolerance surpasses numerical values because it shows how well a trader can manage market price movements. The ability to handle market losses varies between traders because some remain calm during 20% drawdowns but others become anxious with even a 5% decline. The process of defining both financial and emotional boundaries at the start enables strategy development that matches actual possibilities and stops people from giving up on their plans.
Step 2 — Choose your market, timeframe, and trading style
The selection of suitable market conditions and timeframes enables traders to perform their activities according to their available resources and personal characteristics. Major currency pairs such as EUR/USD demonstrate tight spreads and high market liquidity yet exotic pairs tend to experience wider price movements and higher transaction expenses. Traders can preserve their resources through a certain set of instruments which stop capital and attention from being spread too widely.
Traders need to choose their timeframes because this selection decides how often they will trade and what trading methods they will use. Intraday traders track their charts at intervals of 5 minutes or 15 minutes while executing multiple trades throughout each trading day. Swing traders choose to use 4-hour or daily charts for their trading activities because they maintain positions between days and weeks. The process of matching timeframe with availability prevents unmanaged trades from occurring because of time constraints.
Defining a trading style follows naturally. Scalping works best for traders who make fast choices and work with small price differences but position trading suits traders who want to hold positions for extended periods. The best fit framework combines market selection with timeframe and style elements to create a long-term approach which functions across multiple months instead of short-term sessions.
Step 3 — Specify your edge and trade setups
A trading plan requires specific criteria to determine what constitutes a valid trading opportunity. The first step involves locating the “edge” which defines the statistical conditions that lead to advantageous odds for achieving positive results. A confirmed trend on a daily chart with higher highs and higher lows indicates that the edge exists when trading in the direction of the trend. Momentum trading functions as a system to study economic release events for identifying market volatility trading possibilities.
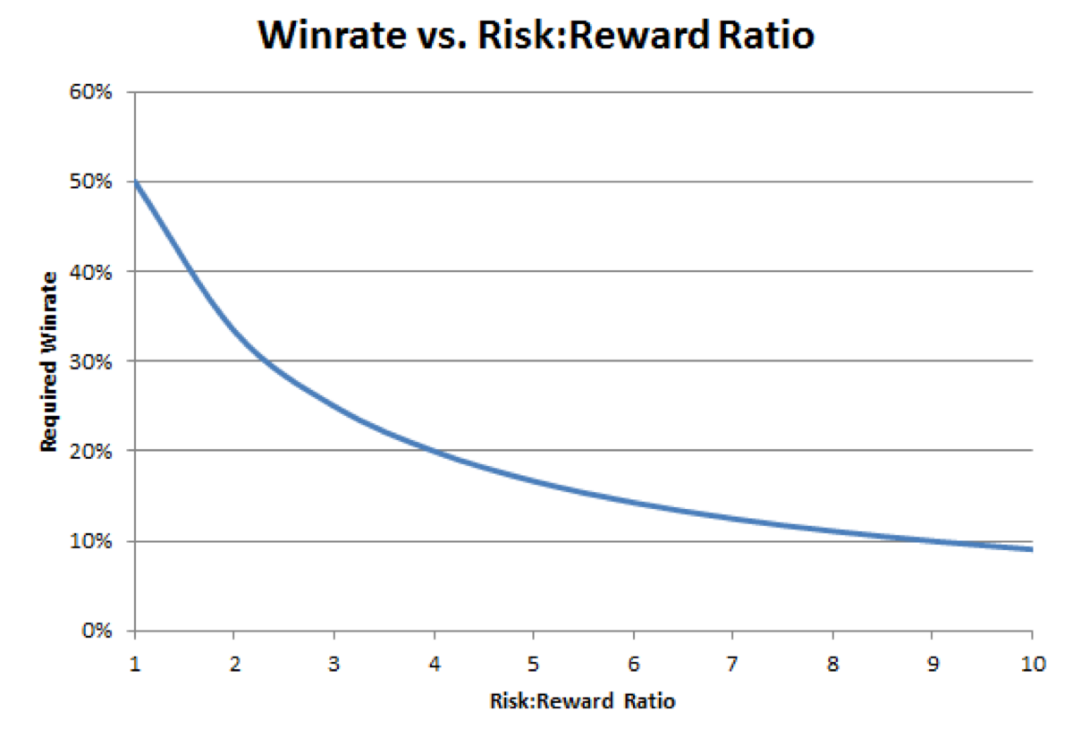
The following step requires a detailed description of all trading positions after establishing the edge. The system includes two main components which are entry triggers that activate when prices exceed resistance levels and exit rules that trigger stop-loss orders below swing low points. The risk-to-reward ratio method allows traders to determine profit targets by risking 50 pips to achieve 100 pips of profit which creates a 1:2 ratio. Documenting trading setups in advance of live trading enables traders to perform their strategies with precision and reduces the chances of making impulsive decisions during market hours.
The system should maintain three reliable setups to avoid excessive complexity. The system requires data-based verification to demonstrate its performance stability across various operational conditions through multiple testing scenarios.
Step 4 — Position sizing, leverage, and risk limits
The most efficient method to manage forex trading risks involves using proper position size management in combination with leverage control. The amount of account funds dedicated to each trade is determined by position sizing but leverage affects both profit and loss magnification. A $10,000 account requires traders to risk no more than $100 per trade when using 1% risk per trade. The stop-loss at 50 pips would result in each pip having a value of $2 which would determine the position size to 0.2 lots.
Leverage needs appropriate management. A broker enables traders to use leverage at 30:1 which means a $1,000 margin can manage $30,000 in currency. The investment strategy provides higher potential returns but it makes the portfolio more sensitive to market changes. The system protects the account from excessive risk through its combination of reduced leverage and pre-set stop-losses which prevent any trade from growing too big.
Risk limits need to reach further than the boundaries of single trade. The practice of establishing daily or weekly loss limits helps traders maintain discipline when markets experience high volatility. The systematic method safeguards investment capital while enabling traders to maintain continuous trading.
Step 5 — Execution standards and broker due diligence
The quality of execution stands as the deciding factor which turns planned results into actual outcomes. Any trading strategy needs a reliable trade execution system to achieve success even when its initial design quality is not optimal. The definition of execution standards involves selecting between market orders for fast execution and limit orders for precise entry points. The evaluation of slippage and spreads and commissions plays a vital role because these costs directly reduce the total net performance. The average spread increase of half a pip on a high-frequency strategy will lead to reduced profitability.
The selection of a broker stands as a critical factor for this process. A regulated broker protects clients through two main measures: it separates client funds from company assets and it discloses all costs in full detail. Checking whether the broker is licensed under trusted authorities ensures that trading is conducted under strict oversight. Traders can find their ideal brokers by evaluating how fast their executions occur and reviewing historical market spreads and available market liquidity.
The process of due diligence needs to include platform reliability as one of its components. The system maintains stability during market fluctuations because its features operate effectively on established trading platforms such as MT4 and MT5. The trading plan operates successfully in actual market environments when traders maintain discipline in their execution and choose suitable brokers.
Step 6 — Pre-trade, in-trade, and post-trade routines
The implementation of trading routines during each stage of trading development enables traders to convert their plans into actual daily trading activities. The pre-trade routine consists of checking the economic calendar and marking important technical levels and creating different market outcome scenarios. The central bank announcement requires developing scenarios for dovish and hawkish outcomes which must include detailed entry and exit strategies for each scenario.
The main goal of in-trade management is to achieve consistency. The process requires tracking how the market behaves in relation to the initial setup and the established rules for making adjustments. A rule exists to enable stop-loss relocation to breakeven points when a trade achieves a one-to-one risk-to-reward ratio. The established rules function as a barrier against sudden market changes during times of market volatility.
A post-trade routine holds the same level of importance as the pre-trade routine. The process of recording each trade with entry and exit points and size and reasoning creates an important performance tracking system. The collected data shows which configurations deliver the most effective results and which areas require additional development. The structured routine enables each trade to build skills and develop discipline through their specific activities.
Conclusion
The process of creating a trading plan marks the start but traders need to stick to their plan to achieve lasting market success. A complete plan consists of defined objectives and risk limits and setup details and scheduled preparation and review procedures. The system contains various interconnected elements which function to minimize uncertainty while providing traders with an organized structure to make their trading decisions.
A trader who dedicates themselves to using the plan for thirty straight trading sessions. At the end of this period, reviewing outcomes against the original rules highlights strengths and areas needing adjustment. The system functions through a feedback system which enables strategies to advance through evidence-based choices instead of emotional reactions.


