Smart money concepts (SMC): How banks trade forex
Smart Money Concepts refer to analytical frameworks that focus on how large institutional participants interact with the foreign exchange market. The study includes banks and liquidity providers and hedge funds and central banks which operate with big transaction amounts to shape market prices through their trading activities. The operations of institutional trading differ from retail trading because they use large position sizes and they need to manage risk transfer and execute trades efficiently.
In the spot forex market, prices move because buy and sell orders are matched. The market requires price adjustments when big orders appear because it needs to discover sufficient market liquidity. The mechanism shows why banks need to understand volume and order flow and market structure when they perform currency trading operations.
What smart money concepts really mean
Smart Money Concepts describe a way of reading the forex market by focusing on how large participants execute trades rather than on indicator signals. The basic principle indicates that prices will move toward areas which contain sufficient liquid funds for making major trading transactions. Banks and institutional desks need to follow a particular market entry sequence because they need to control their trading volume and risk thresholds and choose appropriate trading partners.
A bank needs to establish exposure that matches 10 standard lots which amount to 1,000,000 currency units. Entering this order at once could move price unfavorably. The execution process takes place through different market segments which already have operating buy and sell orders. These areas appear in trading charts which show price movements near their highest points and lowest points and periods of market stability. The market becomes more liquid when prices enter these specific areas because it becomes simpler to execute big trading orders.
The Smart Money Concepts system allows investors to avoid market trend peak and bottom predictions for their investments. The analysis focuses on determining the reasons which cause price to stop or start moving or change direction. A standard lot of 10 pips would translate to approximately 100 units of account currency. The execution of small institutional price variations requires both high performance in execution and strong risk management systems.
How the institutional forex market operates
The institutional forex market functions as a decentralized network where banks, dealers, and liquidity providers quote prices to one another. The execution of transactions happens mainly through interbank platforms and electronic communication networks which use real-time market supply and demand to determine their prices. The three essential factors for institutional trading include execution quality and transaction cost and risk transfer.
The institution needs to expose five standard lots which amount to 500,000 units of currency. The execution process breaks down market impact into multiple small trades instead of using one large visible order. The entire process depends on the precise measurement of every single pip at this operation level. The standard lot system shows that one pip movement equals 10 units of account currency so a five-pip difference will significantly impact trading results.
The management of balance sheet efficiency through margin and leverage operations functions as an alternative to the goal of achieving maximum risk exposure. The system requires 100,000 units to manage margins because it operates with 10:1 leverage to handle 1,000,000 units while maintaining both exposure and drawdown limits at their most stringent levels. The system demonstrates how price movements become rapid in areas with high liquidity because these regions allow investors to execute their position changes at high speed.
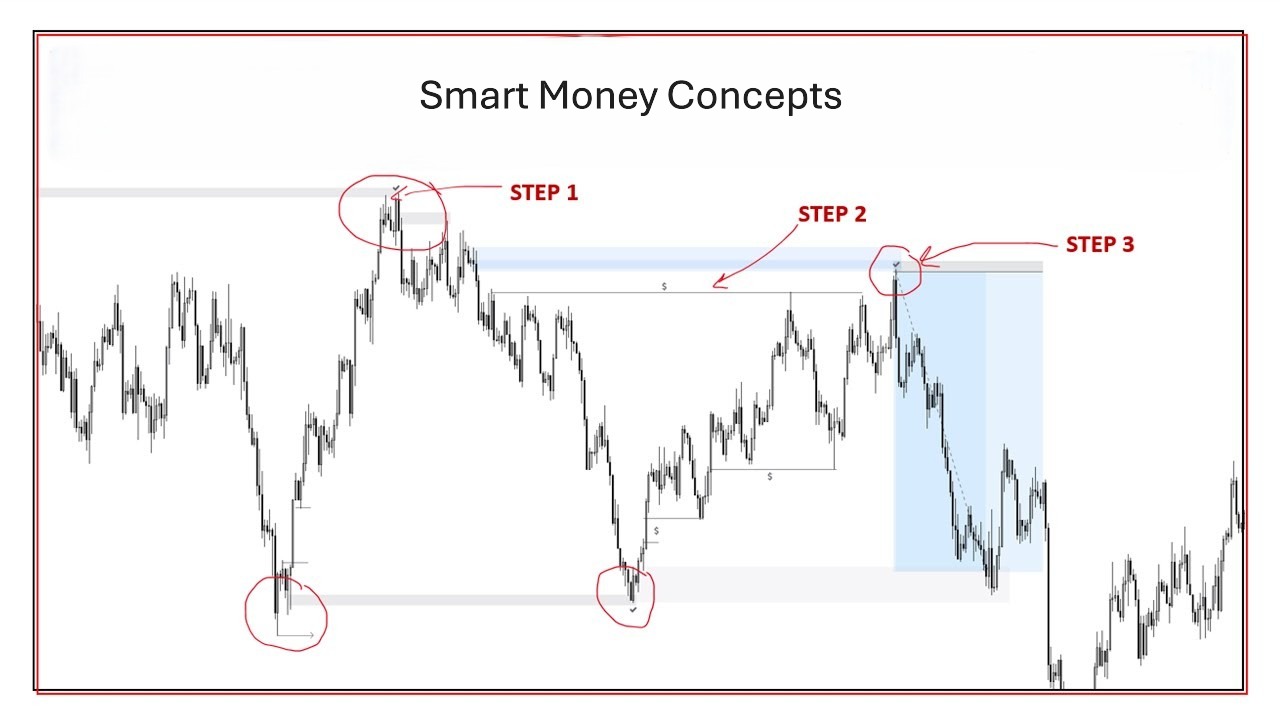
Liquidity as the core driver of price movement
Liquidity refers to the availability of buyers and sellers at different price levels. The forex market shows price fluctuations because traders need to locate identical trading positions for their market transactions. The execution of big trades becomes possible when there is enough money available in the market because it does not cause major price changes. Market prices experience rapid changes because small market transactions become able to affect market values when liquidity stays at minimal levels.
Let’s say price approaches a recent high where many pending sell orders exist. This area often attracts liquidity because traders place stops and limit orders there. If an institution wants to buy several standard lots, this zone provides enough opposing orders to absorb that volume. As orders are filled, price may pause, reverse, or accelerate depending on how much liquidity remains.
The standard lot size equals 100,000 units according to the system. A single pip on that position is typically worth about 10 units of account currency. The execution of multiple lots makes a five-pip change into a significant factor. The value of liquidity zones surpasses the worth of any single price point.
Order flow and institutional positioning
The market receives buy and sell orders through order flow which shows how these orders meet at various price points. The study of institutional trading order flow helps traders locate optimal positions for their trades while they reduce market price movements. The system operates through direct links which affect both market liquidity and trading execution speed.
The institution wants to boost its market exposure through three standard lots which amount to 300,000 units of currency. The research aims to determine which market areas would show conflicting market order entries. When buy and sell interest is balanced, trades can be executed more efficiently. The price system adjusts its rates when orders reach their completion point based on current market supply and demand levels.
The system enables users to track price fluctuations of five pips which affects different lot sizes to generate quantifiable results. On one standard lot, a single pip is worth about 10 units of account currency. The same movement pattern throughout three different areas results in approximately 150 units of movement. The exposure becomes controllable through margin and leverage systems which need small capital investments but traders need to maintain their predetermined position sizes and risk limits.
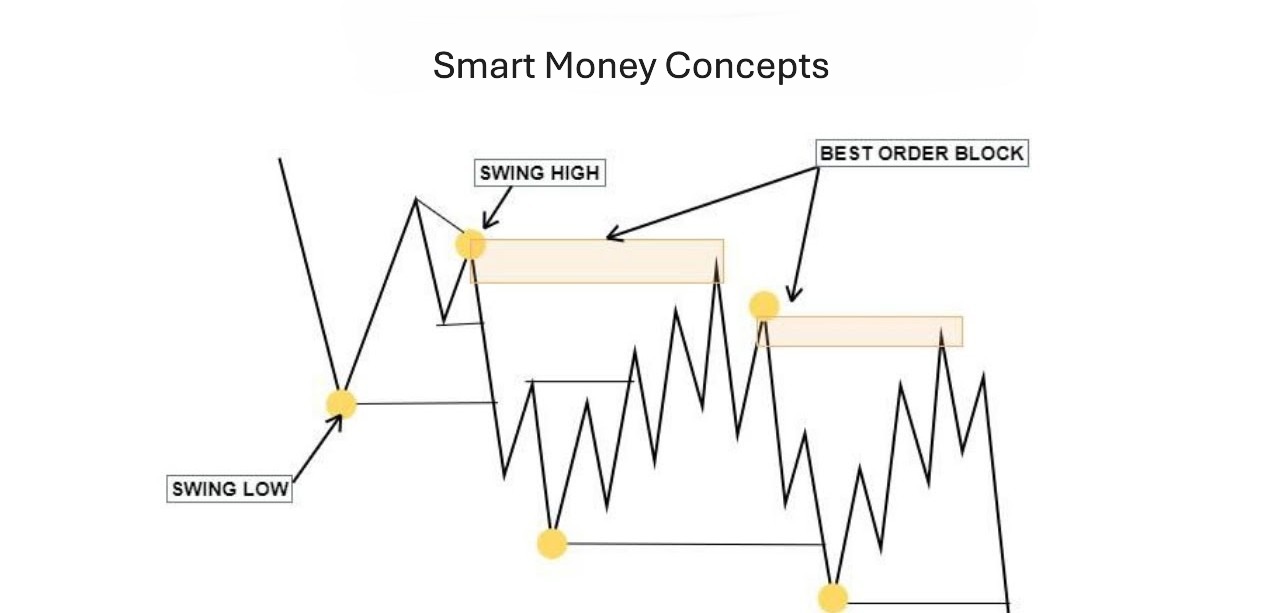
Market structure from a smart money perspective
Market structure determines price behavior across time because it reveals how trading participants make their market entry decisions. The institutional framework shows which major market positions exist and demonstrates their movement between different market areas. The analysis focuses on price movements which occur when prices approach their previous high points and low points and periods of market stability.
Let’s say price has been trading within a narrow range for several sessions. The market shows equal interest in buying and selling activities at this time. The market shows sell-side liquidity absorption through price movements which exceed previous levels while maintaining market backing. The different development stages enable institutions to build their presence through a series of advancing stages. For example, entering two standard lots equals 200,000 units. The 10 pip price movement on this position would translate to 200 units of account currency which allows traders to use structure-based entries when prices move slightly.
The management of capital becomes efficient through margin and leverage but the investment structure decides which risks investors will be able to handle. The placement of stops occurs at points which are farther than current market structures because traders want to position themselves for opposing liquidity flows.
Smart money tools vs retail indicators
Smart Money analysis depends on price behavior and liquidity conditions and execution context instead of using signal-based tools. Retail indicators use two methods to analyze previous price data through average calculations and oscillator methods which generate summary reports. These tools enable users to measure momentum and volatility but they fail to reveal the underlying factors which drive price changes and the preferred locations for big market transactions.
The retail indicator shows overbought market conditions when prices experience a strong upward movement. At the same time, price approaches a previous high where sell orders and stop orders are concentrated. The Smart Money area continues to be relevant because investors can access liquid assets although the indicator has not reached its threshold. The main focus of institutions involves checking if there are sufficient opposing orders which enable them to perform multiple lot entries and exits with efficiency.
For example, trading two standard lots equals 200,000 units of currency. A five-pip difference equals roughly 100 units of account currency. The execution area which exists near liquid zones leads to major changes in market results regardless of how long the price appears on indicator charts. The level of exposure in trading depends on margin and leverage but the actual risk comes from how well an investor executes their trades.
Conclusion
Smart Money Concepts provide a systematic method to analyze price movements through the analysis of market liquidity and order flow and market structure instead of depending on individual signals. The framework reveals price behavior patterns when used properly because it shows how prices move through different levels which attract substantial trading activity.
The trade will use half of a standard lot which amounts to 50,000 units. If the stop is set at 12 pips, the risk is roughly 60 units of account currency. The process of determining lot size and pip value and margin requirements before trading helps traders maintain their trading risk within safe limits of their available account funds. The system operates in the same way as institutional discipline does but it functions at the level of retail operations. Smart Money Concepts function optimally when investors use these methods together with risk management approaches and particular investment goals.


