The role of central banks in forex markets
The Federal Reserve (Fed) together with the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Bank of Japan (BoJ function as central banks to determine currency exchange rates. The main responsibility of central banks includes maintaining price stability and supporting economic growth and managing inflation levels. Central banks implement various monetary policy tools to reach their goals which either directly or indirectly affect exchange rates.
Interest rate modifications affect how attractive a currency appears to investors. The strength of a currency increases when a central bank raises interest rates because foreign investors bring in capital to benefit from higher returns. The value of a currency tends to decrease when interest rates drop because investors lose interest in holding it. Central banks use open market operations and foreign exchange interventions and forward guidance to create major volatility in forex markets.
What are central banks?
A central bank functions as the national monetary authority which implements monetary policy and controls money circulation and maintains financial stability across the country. The main goals of central banks include inflation control and employment maintenance and economic expansion promotion. The operations of central banks differ from commercial banks because they do not provide services to individual customers. The institution operates by supervising banks and conducting business with government bodies and financial market entities.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) operates as the central bank of the United States while the European Central Bank (ECB) serves the Eurozone and the Bank of Japan (BoJ) functions as Japan's central bank. The degree of independence varies between these institutions. The Federal Reserve operates with decision-making autonomy that protects it from political interference thus enabling better long-term economic planning. Central banks in emerging markets sometimes encounter political interference which weakens their policy impact and reduces market confidence.
Central banks maintain the benchmark interest rate as their fundamental operational responsibility. The benchmark interest rate functions as a reference point which determines borrowing and lending expenses throughout the economy. A central bank raises interest rates to combat inflation above target levels because this action reduces spending and lowers prices. The economy experiences growth acceleration through interest rate reductions which occur during economic slowdowns.
How central banks influence forex markets
Central banks control currency values through multiple instruments but interest rate decisions stand as their most powerful tool. A central bank implements interest rate increases as one of its main policy tools. The currency value of a nation tends to rise when interest rates increase because foreign investors seek higher returns. The U.S. dollar gained strength against major currencies during the Federal Reserve's interest rate increase period from 2022 to 2023.
Open market operations represent a second tool which central banks use to buy and sell government bonds. The financial system receives additional liquidity when central banks purchase bonds which leads to currency depreciation. The sale of bonds leads to reduced financial system liquidity which typically results in currency appreciation. The money supply changes through these actions which leads to currency value adjustments based on market expectations about economic performance.
Central banks use direct market intervention to buy or sell their national currency as part of their exchange rate management strategy. The Bank of Japan together with the Swiss National Bank have used direct market interventions to modify exchange rates and defend their export industries. Developed economies use direct intervention less frequently but this approach continues to send strong signals to traders.
Monetary policy tools and their FX impact
Central banks use monetary policy tools to control currency values. The monetary policy instruments consist of interest rates and quantitative easing (QE) as well as reserve requirements and forward guidance. Each monetary policy instrument functions independently to control economic growth which subsequently influences foreign exchange market prices.
The first step involves expansionary policy. Central banks lower interest rates and conduct asset purchase programs through quantitative easing as their main tools. The central bank aims to boost economic growth through lower borrowing costs. The central bank implements QE by buying government bonds and other assets which leads to an expansion of money supply. The ECB's asset purchase programs between 2015 and 2018 led to euro depreciation because of their expansionary monetary policy.
The main objective of contractionary policy is to control inflation through interest rate increases and liquidity reductions. The U.S. dollar strengthened against major currencies when the Federal Reserve increased interest rates during 2022 and 2023. Foreign investors seek better returns by investing in countries with higher interest rates which leads to increased currency demand and value appreciation.
The actions of central banks follow the guidelines of inflation targeting. The majority of central banks across the world target inflation levels at approximately 2%. The central bank implements tighter measures when inflation surpasses its target level. The central bank tends to adopt looser monetary policy when inflation stays below its target level.
The implementation of monetary policy depends on economic indicators which include GDP growth rates together with unemployment statistics and consumer spending patterns.
How traders react to central bank moves
Traders track central bank decisions because these decisions create instant changes in currency exchange rates. The central bank makes an unexpected decision to increase interest rates. The currency tends to strengthen after this type of monetary policy action because it demonstrates a stronger stance against inflation. The currency experiences buying activity from traders who expect ongoing market strength. The U.S. Federal Reserve's June 2022 decision to increase interest rates by 75 basis points led to a strong dollar rise against both the euro and yen.
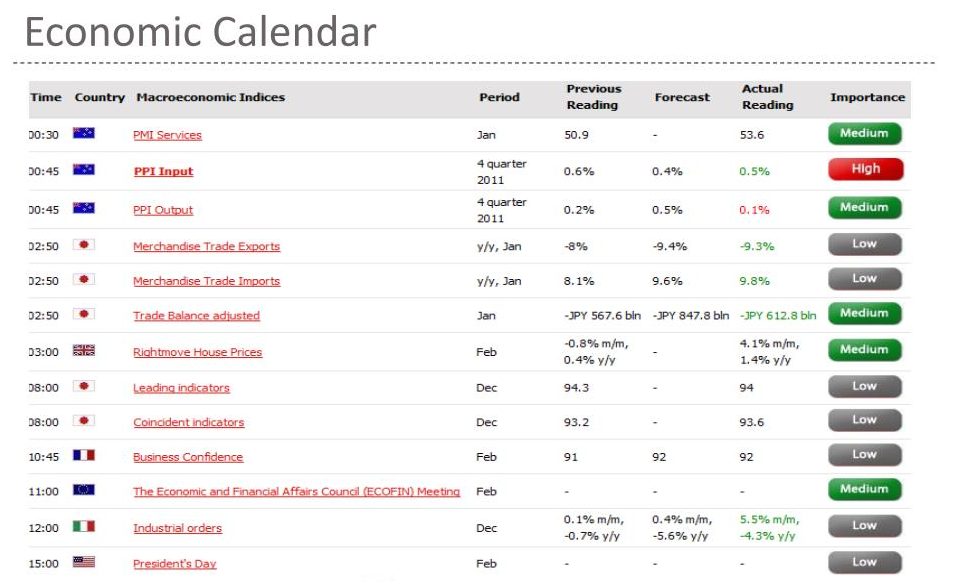
Economic calendars show scheduled events which include central bank meetings together with press conferences. Market prices tend to fluctuate rapidly during these events whenever actual results deviate from predicted outcomes. Traders utilize Economic Calendar tools to prepare for upcoming events which helps them manage their positions effectively.
High-impact announcements require traders to implement risk management strategies as their primary priority. The sudden market fluctuations cause both slippage and wider spreads which affect retail traders who use leverage. The Bank of England's unexpected September 2022 market intervention triggered major GBP/USD market volatility which demonstrates why traders need stop-loss orders and should adjust their trade.
Forward guidance also shapes market sentiment. The market reacts to future policy indications even when no actual policy changes occur. Traders evaluate central bank statements by searching for specific terms including "data-dependent" and "persistent inflation" to understand market sentiment.
Central banks in emerging markets
Forex markets experience distinct behavior from emerging market central banks because these institutions face higher economic volatility and capital flow sensitivity as well as geopolitical exposure. The central banks of developing economies use direct intervention methods to stabilize currency fluctuations and protect investor confidence.
The emergence of a sudden foreign reserve decline combined with rising inflation becomes a scenario for this analysis. The central bank of this nation would increase interest rates substantially to protect its national currency from devaluation. The Central Bank of Turkey implemented a 30% interest rate increase during 2023 to combat inflation and stabilize the lira after a prolonged period of currency depreciation.
The economies that experience currency interventions do so at a higher rate than other economies. The Bank of Russia implements interest rate tools together with capital controls to minimize ruble volatility when geopolitical events occur. Forex traders need to analyze both economic indicators and political events together with external market risks such as commodity price fluctuations in these environments.
The currencies of emerging markets demonstrate greater responsiveness to decisions made by the U.S. Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve's monetary policy tightening leads to capital outflows from emerging markets toward higher-yielding U.S. investment opportunities. The resulting currency weakness and increased borrowing expenses in these economies force them to adopt either preventive or reactive policy measures.
Conclusion
The knowledge of central banks enables traders to enter currency markets with better confidence and accuracy. The decisions made by monetary authorities regarding interest rates and forward guidance and asset purchases directly influence exchange rate movements. The central bank actions follow macroeconomic indicators which include inflation rates and employment statistics and GDP growth data that traders can verify through financial sources.
A trader who notices the Federal Reserve plans to increase interest rates because of sustained inflation can make this prediction. The information leads to a forecast that the U.S. dollar will strengthen in value. Traders who understand policy directions make better trading decisions by matching their market entries and exits with overall market trends instead of depending only on technical indicators.
The upcoming moves of central banks become accessible through their calendars and press releases and speeches. Risk management tools such as stop-loss orders and trade sizing become especially critical around high-impact events. Traders who focus on emerging markets need to evaluate both political risk and foreign reserve dynamics as additional factors.
A trading strategy built from central bank analysis leads to a more organized method of forex market participation. The combination of central bank communication monitoring and economic data updates and historical case study reviews leads to better decision-making.


