Top 5 forex trading strategies that actually work
The term "working" in forex strategy evaluation refers to successful trading outcomes rather than achieving victory in every single transaction. Instead, it refers to having a positive expectancy over time. The expectancy formula uses win rate together with average reward and average risk to calculate the overall balance. A system that achieves 45% success rate while generating double the amount from winning bets than losing bets remains profitable.
A strategy needs to maintain its effectiveness in various market conditions. A trend-following method would succeed in strong directional market movements yet fail to perform well during periods of market stability. The method remains effective when combined with risk management strategies and portfolio diversification. Risk-adjusted returns function as the ultimate success metric which surpasses the value of basic profit numbers.
Finally, transaction costs, slippage, and leverage must be considered. The value of even the most effective rules becomes meaningless when trading spreads become excessive and positions become too large. Sustainable trading requires traders to maintain discipline through proper position sizing techniques.
Strategy 1 — Time-series momentum (Trend following)
Trend following is one of the oldest and most researched approaches in forex. The basic principle states that currencies which have shown significant movement in one direction tend to maintain this trend for some duration. Let’s say the EUR/USD has been rising steadily and breaks above a 50-day moving average. The trader would enter a long position through trend-following system by placing a stop-loss order under the current support level and enabling a trailing stop to maximize profits when the trend continues to rise.
This strategy works best during periods of strong directional movement but can underperform in sideways or choppy markets. Traders apply Average True Range (ATR) as a trade filter because it enables them to avoid times when market momentum remains low. Risk management functions as an essential element because traders modify their position sizes according to market volatility to protect themselves from significant losses when market trends move against their positions.
Strategy 2 — Carry trade
The carry trade focuses on earning the interest rate difference between two currencies. The process of trading involves exchanging a currency with higher interest rates for one with lower interest rates. For example, if the Australian dollar offers a higher interest rate compared with the Japanese yen, going long AUD/JPY allows the trader to collect the daily interest, known as the swap or rollover.
The investment strategy produces consistent return accumulation when market conditions remain stable. However, carry trades are highly sensitive to changes in global risk sentiment. The market value of pairs with positive carry tends to decline rapidly when investors choose safe-haven currencies because this action eliminates all previous months of profit.
Risk management requires traders to use carry with trend or momentum filters which help their trades move in the same direction as market trends. The strategy for position sizing requires market reversal anticipation because carry trades lose substantial value during times of financial market stress.
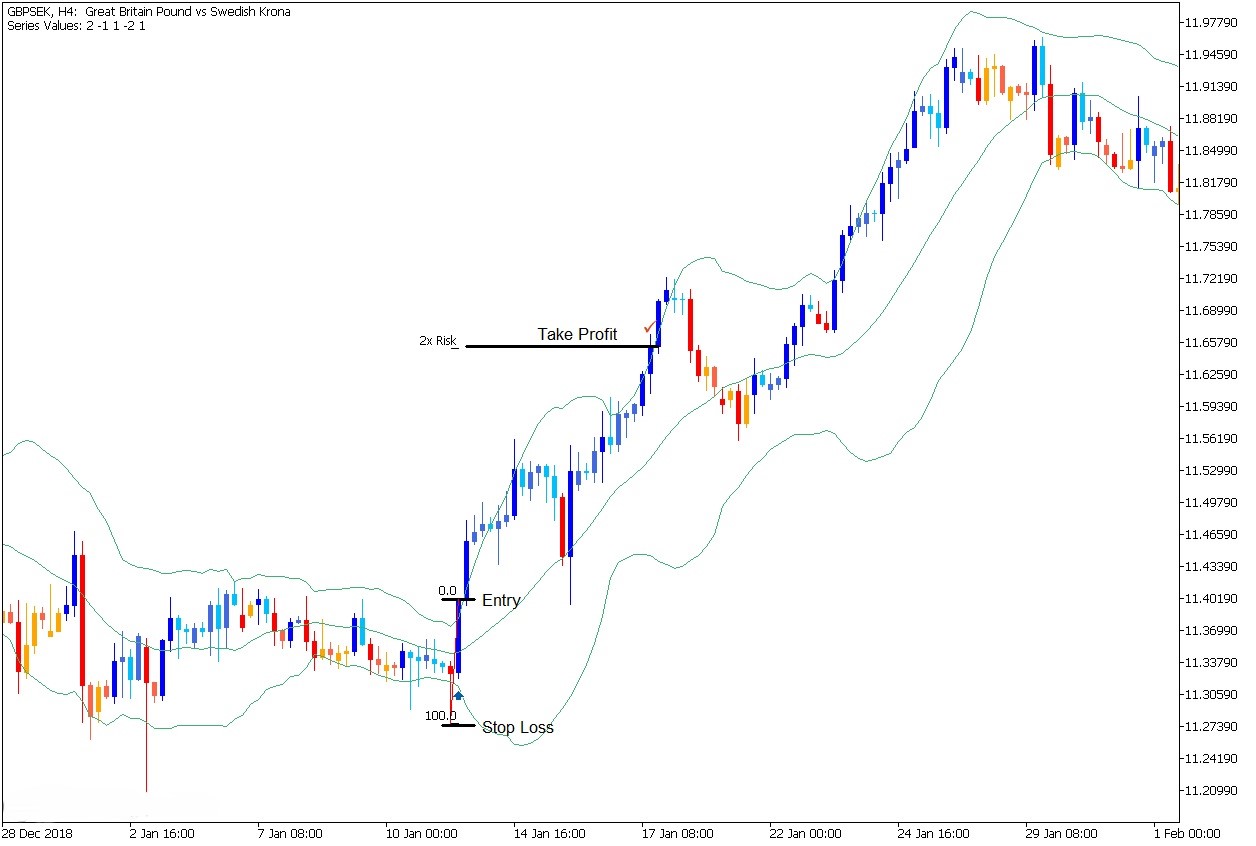
Strategy 3 — Value trading (Purchasing power parity)
Value trading relies on the idea that currencies tend to move back toward their fair value over time. The estimation of fair value depends on purchasing power parity (PPP) which examines the relative prices of goods and services between countries. A currency becomes undervalued when the price of a standard basket of goods is lower in one economy compared to another.
Let’s say the EUR/USD exchange rate trades far below its long-term PPP estimate. A value trader would purchase euros because they anticipate the euro value to increase steadily during a period of months or years. The slow progression of these market movements forces traders to hold their positions for longer durations while they decrease their position sizes for risk control.
The main obstacle in currency valuation stems from the fact that exchange rates can stay misaligned for many months. The risk of entering positions can be minimized when traders use valuation signals together with momentum or trend confirmation indicators. The system stops users from making trades until market direction becomes obvious.
Strategy 4 — Range trading (Mean reversion)
Range trading involves making money from currency pair price movements between established support and resistance levels. This approach works best in stable market conditions when no strong trend is present. A trader would purchase near the lower boundary of 1.2600 to 1.2800 while selling near the upper boundary of this range.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Bollinger Bands serve as indicators to detect when currency prices move beyond their typical price range between overbought and oversold levels. The pair's support test becomes more likely when RSI drops below 30.
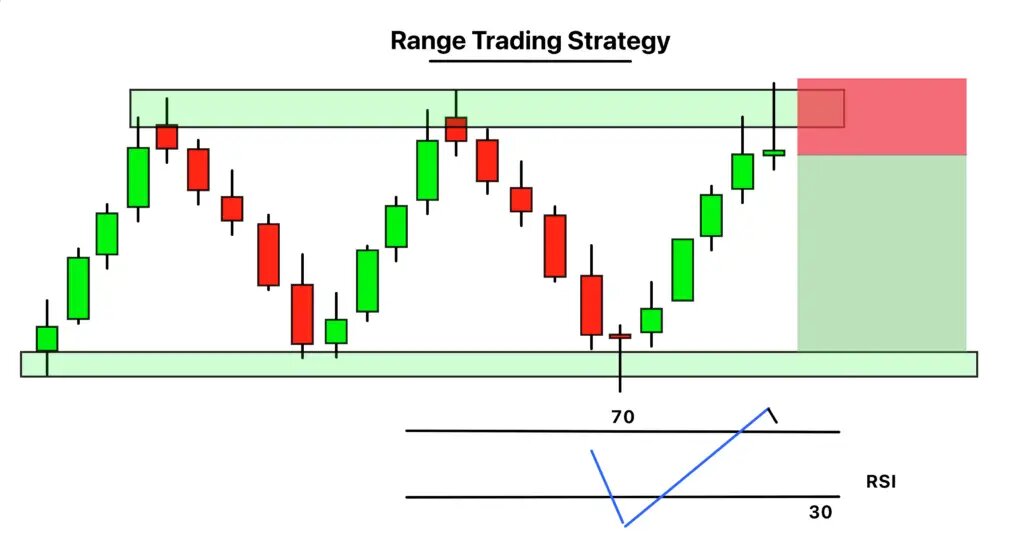 The main risk happens when prices move beyond the established price range in ways that were not predicted. The placement of stop-loss orders outside support and resistance levels serves as a method to handle this situation. The trader uses small position sizes to reduce exposure during times of unexpected market volatility.
The main risk happens when prices move beyond the established price range in ways that were not predicted. The placement of stop-loss orders outside support and resistance levels serves as a method to handle this situation. The trader uses small position sizes to reduce exposure during times of unexpected market volatility.
Strategy 5 — Event-driven trading
Event-driven trading functions through price movements that happen after major economic reports and central bank announcement events. The Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) release along with inflation data and interest rate adjustments trigger major short-term market movements in currency exchange rates. The dollar value will surge quickly when U.S. inflation data surpasses market forecasts because investors believe the Federal Reserve will implement tighter monetary policies.
The main goal should focus on the first peak because it tends to be unstable and may not hold its position. Instead, some traders wait for the market to settle and then trade in the direction of the dominant move. The EUR/USD pair will drop quickly after an interest rate announcement then establish a new support level which will trigger a continuation signal.
Risk management stands as a vital process because market spreads tend to increase during such times. Many traders set hard maximum loss limits and avoid trading less liquid pairs to reduce the chance of extreme price swings.
Risk management, sizing, and portfolio construction
A successful strategy depends on proper risk management to achieve its goals. The main principle requires traders to risk no more than a tiny fraction of their total investment capital for each trading operation. The maximum loss amount would be $100 since the account size is $10,000 and the risk per trade is set at 1%. The investment strategy protects against market downturns while allowing investors to maintain their position in the market for longer durations.
Position sizing is often based on volatility. The EUR/USD pair shows an Average True Range (ATR) of 80 pips in its daily market operations. A stop-loss is set at 80 pips, and with a $100 risk allowance, the position size would be 0.12 lots. This ensures that if the stop is hit, the account risk limit is not exceeded.
Risk distribution becomes possible through the implementation of different investment approaches with various currency pair combinations. The combination of carry trades with trend following methods helps investors decrease their dependence on specific market conditions while generating more stable investment returns.
Execution quality
A well-defined strategy can only deliver consistent results if trade execution is efficient. The quality of execution depends on three main factors which include spreads, slippage and order handling. The initial 3 pips of spread will decrease the trader's potential earnings by 10% before the trade begins to move. The costs of these systems decrease their operational effectiveness with each passing year.
A high-impact news release occurs when an order is placed. Price may move rapidly, and slippage can occur, meaning the trade is filled at a worse level than expected. Traders stay away from new position openings during announcements yet they use limit orders to place their trades.
The broker selection process directly affects the outcome of the transaction. The execution statistics of MetaTrader platforms enable traders to view their average spread and slippage data. A trading journal that includes execution data helps traders identify whether their weak results come from their trading strategy or from the costs of executing trades.
Backtesting and validation
Historical market data evaluation of trading strategies provides evidence about their ability to perform well in actual real-time market conditions. The process requires applying trading rules to past market data to determine success rates and profit amounts and maximum losses. A backtesting of a trend-following system on EUR/USD data from the last ten years would reveal if the system generated positive expectancy in its results.
The results obtained from raw backtesting need validation to stop misinterpretation of their results. The practice of out-of-sample testing serves as a method for traders to prevent curve-fitting because it applies the strategy to data that was excluded from optimization. Walk-forward testing goes a step further by periodically re-optimizing parameters and then testing them in unseen periods.
Common mistakes to avoid
Investors make a major mistake by using past market data to determine their investment approach. The use of exact parameters for moving average crossover system optimization based on a single past period results in system failure when trading live. The solution requires evaluation through multiple time intervals and various combination scenarios.
The process of finding news spikes introduces an additional risk factor into the system. The lack of a defined plan when entering trades during market volatility announcements results in price movements that cause financial losses. Finally, switching strategies too quickly prevents any method from showing its true performance. Forex traders must survive through regular trading activities and proper position management and accurate market comprehension.

 The main risk happens when prices move beyond the established price range in ways that were not predicted. The placement of stop-loss orders outside support and resistance levels serves as a method to handle this situation. The trader uses small position sizes to reduce exposure during times of unexpected market volatility.
The main risk happens when prices move beyond the established price range in ways that were not predicted. The placement of stop-loss orders outside support and resistance levels serves as a method to handle this situation. The trader uses small position sizes to reduce exposure during times of unexpected market volatility. 