Using options to hedge forex exposure
Foreign exchange exposure occurs because exchange rate movements affect the value of assets and liabilities and future business transactions. The forex market shows how small price movements in pips affect financial results when traders use their position size together with leverage and their margin requirements. Let’s say a trader or business holds a long position of one standard lot in EUR/USD. The value of a 50-pip market movement in a specific lot size will always result in financial loss no matter what the trading strategy involves.
The process of hedging helps organizations decrease their market uncertainty while they continue to participate in financial markets. The primary goal of hedging practice requires investors to defend their assets from market downturns while maintaining their ability to benefit from market advances. The process needs options as a protective tool which helps manage price risks through market downturns while offering more flexibility than spot hedges and forwards. The option establishes its maximum possible loss through an upfront premium payment which stays within known limits while spot position margin requirements apply to the entire position.
Overview of currency risk in forex markets
The financial effects of exchange rate changes constitute the risk which businesses face when they deal with currency fluctuations. The risk in forex trading grows stronger because traders use position size and leverage in their trading activities. Let’s say a position of 0.5 lots is opened on USD/JPY. The total loss from a 40 pip exchange rate movement will equal the pip value times the number of pips. The market position continues to offer this position because it fulfills three essential needs which include speculative requirements and defensive needs and operational requirements for handling upcoming payment duties and generating revenue.
Business operations become more complex when it comes to currency risk exposure because companies use margin and leverage strategies in their operations. Traders can handle larger theoretical values through leverage because they only need to post small margin amounts but they must bear all market-related risks. The 20:1 leverage enables traders to protect their entire margin during any 5 percent market price fluctuation. The risk associated with currency fluctuations differs between different currency pairs. The volatility of major currency pairs remains lower than emerging market currencies but these pairs experience sudden market fluctuations when economic data becomes available and when interest rates change and when geopolitical incidents happen.
Fundamentals of forex options
The Forex options market offers derivative instruments which grant investors the right to execute currency pair transactions at predetermined exchange rates during set timeframes. The agreed exchange rate which investors use to buy options is known as the strike price and the premium represents the initial payment made to obtain this right. The risk management process for options operates differently than spot positions because options do not need full notional value margin which alters their risk management approach.
Let’s say exposure exists to one standard lot of GBP/USD. The exposure needs a unique method of management because investors use call and put options to determine their highest possible loss instead of using direct spot market offsetting. The premium payment serves as the maximum amount which can be lost when market conditions become unfavorable. The option remains unused when market conditions become favorable but investors will exercise it based on their investment approach.
The value of options depends on four main elements which include time until expiration and market volatility and interest rate variations and the current market value in relation to the strike price.
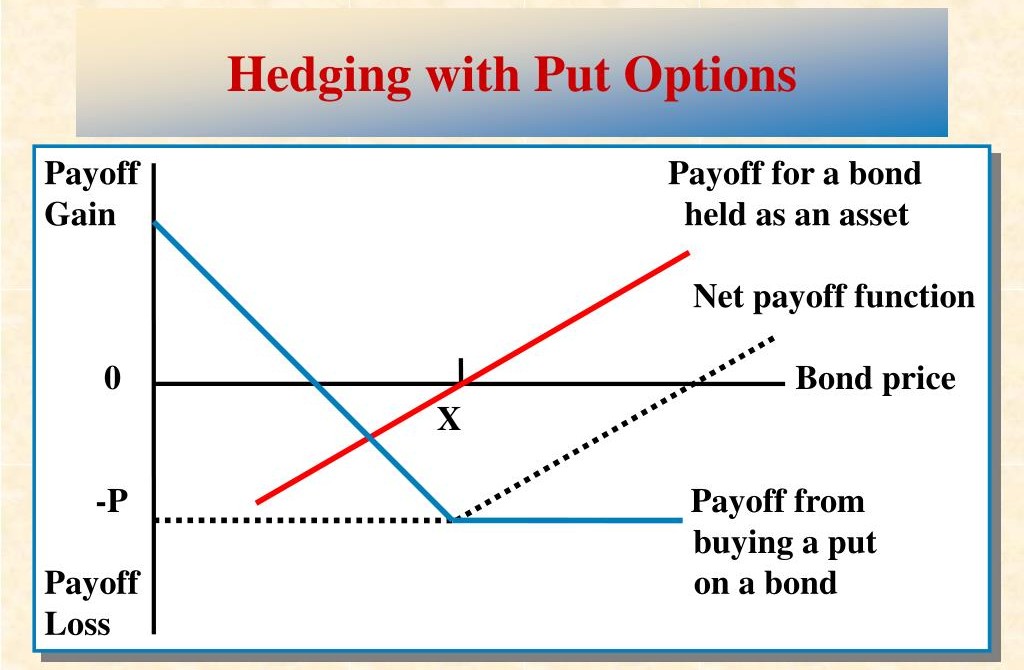
Key types of options used in currency hedging
Two primary option types are commonly used to hedge forex exposure: call options and put options. A call option provides the right to buy a currency pair at a fixed exchange rate, while a put option provides the right to sell at a fixed rate. The selection process depends on which way the fundamental market exposure is moving.
The upcoming payment will use euros as its currency. A call option on EUR/USD can protect against a rise in the euro. The option provides protection when the exchange rate rises because it reduces the impact of the higher exchange rate. If the exchange rate falls, the option can be left unused, and the lower spot rate applies. The maximum loss remains limited to the premium paid.
Options are also classified by exercise style. European-style options have expiration as their only exercise time but American-style options enable holders to exercise their options at any point during the remaining time until expiration. European-style options are more common for structured hedging due to simpler pricing.
How options function as a hedging instrument
The Options function operates as a hedging tool because it enables users to move specific currency risks into expenses which they can predict. The initial payment for the option premium functions as the maximum amount which the hedge will ever lose. Options require different margin calculations than spot positions because they do not need full notional value margin which enables better control of exposure.
Let’s say exposure exists to one standard lot of USD/JPY due to a future cash flow. A put option can be purchased to protect against a decline in the exchange rate. The option value will increase when USD/JPY experiences a 60 pip decline because this change will reduce the loss from the underlying position. The option will remain unused when the exchange rate increases but the investor will gain from the positive change in the spot market. The premium stands as the single expense which remains constant.
This structure allows downside risk to be capped while keeping upside potential open. The hedging duration of options enables investors to match their hedging strategies with their required time periods which include both monthly settlement dates and quarterly financial reporting cycles.
Common forex hedging strategies using options
The market uses structured investment methods which combine options to protect against currency changes at affordable prices while reducing possible risks. The protective option serves as a standard solution which people tend to use. Let’s say exposure exists to one standard lot of AUD/USD due to a future conversion. A put option can be purchased to lock in a minimum exchange rate. The investment protection from currency value decreases is what this option provides. The currency strength does not affect the spot gain because the premium functions as the exclusive expense.
The collar strategy functions as a trading approach which requires investors to buy defensive options while they sell options with various strike prices. A put option purchase serves to protect against market declines while selling a call option helps decrease the total premium cost. This structure narrows the exchange rate range but lowers upfront cost.
Options can be used to create multiple investment periods which extend from different time frames. This allows exposure tied to monthly or quarterly cash flows to be hedged gradually rather than all at once. The selection of an appropriate strategy needs three vital elements to be evaluated which are exposure size and time horizon and acceptable risk range.
Cost, premiums, and risk considerations in option hedging
The primary cost of using options for forex hedging is the premium paid upfront. The premium value depends on market volatility and the remaining time until expiration and interest rate differences and the current exchange rate distance from the strike price. The premium functions as a specific known value which enables traders to understand their risks during the first stages of trading.
Let’s say a put option is purchased to hedge one standard lot of EUR/USD with a premium equal to 30 pips. The maximum loss from the hedge will not exceed 30 pips even when the exchange rate moves 200 pips against the underlying exposure. The value of unhedged spot positions decreases continuously when market prices shift away from their initial value.
The security features of affordable solutions do not extend to provide complete protection. Options with strike prices far from the current market level are cheaper but only become effective after a significant price move. Balancing premium cost against desired protection is a core risk management decision. Evaluating different strikes and expirations helps align hedging costs with acceptable risk levels and financial objectives.
Conclusion
Options serve as a defined method to handle foreign exchange risks which traders and operational teams can quantify. Options investors can use these tools to convert unpredictable market price changes into fixed costs which defend their assets from market declines while allowing them to benefit from market expansion. The balance needs most attention during the process of determining exposure size and leverage and timing because exchange rate directions for the future remain unknown.
The exposure factor consists of two elements which include current investments and regular monthly cash payments that take place when major economic announcements occur. The risk profile becomes more predictable when traders use established timeframes for option expiration dates and lot sizes instead of depending on spot adjustments. The premium functions as a fixed cost which customers understand yet the protection against market volatility remains limited to the pre-defined coverage amount. This clarity supports more consistent planning and disciplined execution.


