What is Elliott Wave in Forex Trading
Elliott Wave Theory was developed by Ralph Nelson Elliott back in the 1930s. He challenged the accepted belief at the time that financial markets behaved in random and chaotic movements.
Elliott believed sentiment and psychology were the most prominent drivers and influences on market behaviour. Therefore, in his opinion, it was possible to find structure and patterns in the market.
Ninety years after his discovery, many traders place faith in Elliott’s theory. Here we’ll discuss aspects of the Elliott Wave principle, including applications in today’s fast-moving forex markets.
Basic Elliott Wave Theory facts
The Elliott Wave Theory is a method of technical analysis searching for recurring long-term price patterns related to investor sentiment and psychology changes.
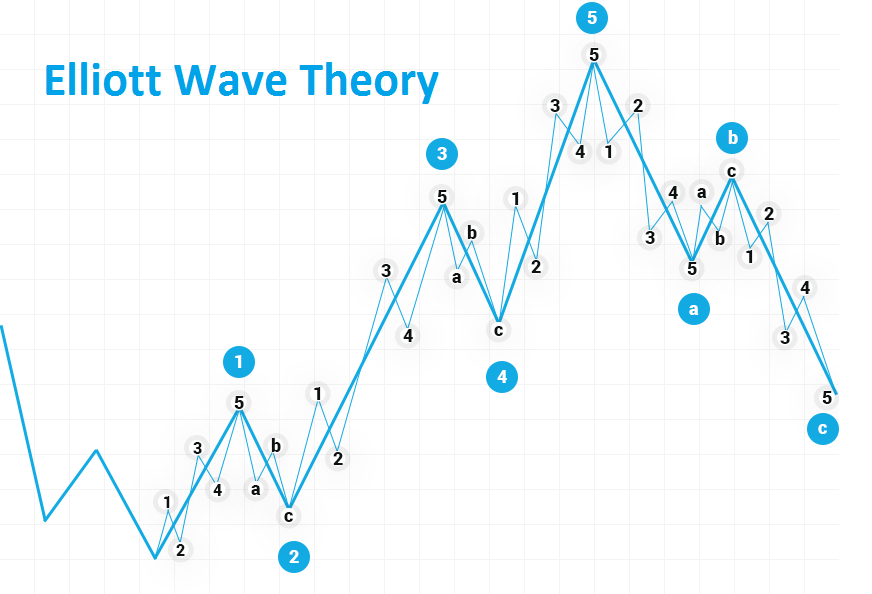
The theory identifies two types of waves. The first is called impulse waves that set up a trend pattern—followed by corrective waves which oppose the underlying trend.
Each wave set gets contained inside a more extensive group of waves that stick to the same impulse or corrective pattern.
The basics of Elliott Wave
- Elliott proposed that prices of financial assets trend due to investors’ psychology.
- He asserted that swings in mass psychology continually repeat in the same recurring fractal patterns (or waves) in financial markets.
- Elliott’s theory was similar to Dow theory as both suggest stock prices move in waves.
- However, Elliott went deeper by identifying fractal behaviour in markets, allowing him to apply deeper analysis.
- Fractals are mathematical structures, which infinitely repeat themselves on a diminishing scale.
- Elliott claimed price patterns in assets such as stock indices behaved the same way.
- He then suggested these repeating patterns could predict future market moves.
Market predictions using wave patterns
Elliott calculated his stock market predictions based on the characteristics he spotted in wave patterns.
His impulse wave, which travels in the same direction as the larger trend, has five waves in its pattern.
On the other hand, the corrective wave moves in the opposite direction of the dominant trend.
Elliot identified five more waves within each of the impulsive waves, and he theorised that this pattern repeats itself to infinity at ever-smaller fractal amounts.
Elliott discovered this fractal structure in financial markets in the 1930s, but it took decades for scientists to recognise this phenomenon as fractals and use them mathematically.
In financial markets, we know what goes up eventually comes down. Whether it’s up or down, a price movement should always get followed by a contrary motion.
Price action in all its forms can get divided into trends and corrections. The trend shows the main direction of price, while the corrective phase moves against the underlying trend.
Elliott Wave Theory application
We can break down the Elliott Wave like this.
- Five waves move in the direction of the primary trend, followed by three waves in a correction (totalling a 5-3 move).
- The 5-3 move becomes subdivided into the next higher wave move.
- The underlying 5-3 pattern remains constant, but the period of each wave may vary.
- In total, you get eight waves, five up, three down.
An impulse wave formation, followed by a corrective wave, forms the Elliott Wave principle consisting of trends and countertrends.
Five waves do not always travel upward, and the three waves do not always travel downward. When the larger-degree trend is down, the five-wave sequence can also be down.
Elliott Wave degrees
Elliott identified nine degrees of waves, and he labelled these from largest to smallest:
- Grand Super Cycle
- Super Cycle
- Cycle
- Primary
- Intermediate
- Minor
- Minute
- Minuette
- Sub-Minuette
Because Elliott waves are fractals, the wave degrees could theoretically expand ever-larger and ever-smaller above and beyond the list above.
Simple forex trading idea using Elliott Wave Theory
A trader might identify an upward-trending impulse wave and go long to apply the theory to everyday forex trading.
Then they would sell or short the position as the pattern completes its five waves, suggesting a reversal is imminent.
Does Elliott Wave work in forex trading?
The Elliott Wave Principle has its devotees and its detractors like all other analysis methods.
Just because markets can get analysed down to a granular fractal level does not make financial markets more predictable using Elliott Wave.
Fractals exist in nature, but that doesn’t mean anyone can predict the growth of a plant or that it’s 100% reliable when trading forex currency pairs.
Practitioners of the theory can always blame their losing trades on their reading of the charts or irrational and unpredictable market behaviour rather than weaknesses in Elliott Wave theory.
Analysts and traders might find it tricky to identify the specific waves on their charts, whatever timeframes they use.
Elliot Wave strategies
There are straightforward rules to follow for the Elliott Wave count to get confirmed:
- Wave 2 should never retrace more than 100% of wave 1.
- Wave 4 should never retrace more than 100% of wave 3.
- Wave 3 needs to travel beyond the end of wave 1, and it’s never the shortest one.
If the initial five-wave movement is clearly defined, we can identify the various corrective patterns.
Corrective patterns come in 2 shapes: sharp corrections and sideways corrections because the patterns get classified into three main categories: flat, zig-zag and triangle. So, let’s discuss the three classifications in more detail.
Elliott Wave Flat Pattern
The Elliott Wave flat pattern is observed in three forms, regular, expanded and running. This pattern moves against the primary trend direction, typically appearing at the end of the cycle. Traders expect a continuation of the wave and momentum in the direction of the underlying trend.
Let’s now concentrate on the regular flat corrective pattern seen in uptrends. The main rules Elliott Wave pattern must follow in this form are:
- Wave B always stops near the original starting point of wave A.
- If there’s a break above this point, we have an irregular or expanded flat.
- Wave C always breaks below the endpoint of wave A.
Elliott Wave Zig-Zag Pattern
An Elliott Wave zig-zag pattern is a three-wave structure labelled ABC subdivided into 5-3-5 waves of more minor degrees.
- Both waves A and C are classed as impulsive waves, while wave B is a corrective wave.
- Wave C generally travels the same distance in price as wave A.
- It typically develops in wave 2 of the 5-wave cycle.
Elliott Wave Triangle
The final pattern is the triangle pattern which is a form of prolonged sideways action in the market.
This pattern tends to appear more frequently in wave 4 of the 5-wave cycle.
Let’s analyse the following rules must confirm the ascending triangle, which becomes established when the following patterns get created.
- The triangle exhibits a clearly defined ABCDE wave pattern.
- Each wave gets subdivided into 3 waves of more minor degrees.
- A is the original peak, then B becomes the new high peak.
- After B gets reached, a corrective wave pattern gets formed.
- C becomes the low printed in the series, below the original A peak.
In summary, Elliott Wave Theory/Principle is no better or worse than many other technical analysis tools at your disposal.
It would help if you took on board that the theory was developed nearly a century ago by an analyst who advised using it on weekly and monthly time frames.
The volatility seen in the markets and the trading volume then was a fraction of what we experience today.
Many fans of Elliott’s theory would suggest that the idea has more credibility in today’s busier markets because patterns should be more pronounced. And in some ways, they’d be right. Market sentiment is a crucial driver of price action in all financial markets.
Click on the button below to Download our "What is Elliott Wave in Forex Trading" Guide in PDF

