What is forex trading and how does it work
Forex trading (In short) simply means the exchange of one foreign currency for another currency with the aim of making profits from their relative price movement.
The understanding of how forex trading works begins with learning the basics and having solid background knowledge of forex.
Comprehensive fundamental tutoring is very crucial in the odyssey to attain a level of consistent profitability.
There are various means to trade foreign exchanges either physically, in a bank, online payment platforms, online exchanges or forex brokers trading platforms, of which the latter provides seamless trading opportunities covering many financial market asset classes - bonds, stocks, currencies, commodities e.t.c.
The forex market is known to be the world's largest and most liquid financial market, with trillions of dollars traded daily. It currently holds an estimated global daily turnover of more than US$6.5 trillion rising from $5 trillion in just a few years.
The market is open for 24 hours of trading, every 5 days (Monday to Friday) of the week, for institutional banks, commercial hedgers, institutional investors, hedge funds, large speculators and retail traders to buy and sell currencies, stocks, bonds, indices, metals and other securities.
What makes the forex market unique is the decentralization of networks and the electronic trading via computer networks known as an Over The Counter (OTC) market.
Stick through to the end of this article as we walk you through the basics of how forex works.
Types of foreign exchange market
Foreign exchange trading in the financial markets is of three different types
- Spot forex market:
This is an off-exchange market for spot trading or spot transactions.
Spot trading refers to the buying and selling of foreign currencies, financial instruments, or commodities for instant delivery on a specified spot date. This involves the physical delivery of a traded asset when the trade is settled.
The exchange rate on which these transactions are based is referred to as the Spot Exchange Rate.
The spot market is dominated by banks and large institutions, but Forex derivatives are offered by brokers based on spot forex prices.
- Forward forex market:
This is an over-the-counter marketplace where there are private agreements to buy or sell a certain amount of currency at a particular price for future delivery at a certain time.
- Futures forex market:
This is similar to the forward forex market, except that contracts can be traded on futures exchanges.
Currency pairs (Base and Quote currency)
A currency pair refers to two currencies traded in pairs. This implies that one currency is sold in order to buy another and vice versa. Each currency in a pair is represented by a unique three-letter code.
The first currency code of a currency pair is the base currency while the second currency of the pair is called the quote currency.
You can identify a country and its currency by the letters of the code.
For example;
GBP. GB represent Great Britain and P represents ‘Pounds'
USD, US represent the United States and D represents Dollar
Although there are exceptions to this, EUR represents the continent of Europe and its currency “the Euro”.
Forex Prices
Forex prices refer to how much one unit of the base currency is worth in the quote currency. This is also known as the exchange rate because it expresses the value of one currency in terms of the other at a certain time.
For instance, the current price of USD/JPY can be quoted at 0.6191.
Where the price of one unit JPY (base currency) is worth the value of USD (the quote currency).
If USD/JPY was trading at 0.6191, then 1 JPY will be worth 0.6191 USD at that time.
If USD rises against the YEN, then 1 USD will be worth more YEN and the price movement of the currency pair will move higher but on the contrary, if USD drops, the price movement of the currency pair will also drop.
Hence if your technical and fundamental analysis predicts that the base currency is likely to strengthen against the quote currency, you can open a long position on the currency pair and you can also open a short position on the currency pair if your analysis predicts bearishness on that currency pair.
How currency pairs are sorted
Almost all forex trading platforms categorize forex pairs based on popularity, frequency of trading activities and price volatility.
- Major pairs: These currency pairs are referred to as “the majors” because they are the most traded currency pairs and they account for approximately 80% of global forex trading. They include EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/CAD, USD/JPY, AUD/USD and USD/CHF
- Minor pairs: These are strong economic currencies paired against each other and not the US Dollar. They are less frequently traded than the USD pairs. Examples are EUR/CAD, GBP/JPY, GBP/AUD e.t.c.
- Exotics: These are pairs of major currencies against currencies of weaker or emerging economies. Examples are AUD/CZK (Australian dollar vs ), GBP/MXN (Sterling vs Polish zloty), EUR/CZK
Forex trading sessions
The forex market is run by a global network of banks, spread across four major cities of different time zones in different parts of the world: London, New York, Sydney and Tokyo.
Therefore some currency pairs have significant trading volume whenever it's the trading sessions (periods) linked to that region.
The different cities have overlapping trading sessions. Below is the sweet spot of these trading sessions to scout for profitable trade setups.
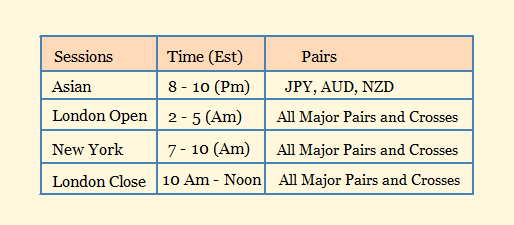
The forex market is decentralized and can be traded remotely 24/7 from 5 p.m. EST on Sunday until 4 p.m. EST on Friday.
Trading Forex Also Involves the following important concepts
- Pip
In the foreign exchange market, PIP, short for Percentage In Point or Price Interest Point, is a measure or unit of change in the exchange rate of a currency pair.
It is the smallest possible move of the price of a currency pair which is the equivalent of a ‘Percentage In Point’ of price movement.
- Spread
Spread is the cost of trading which is the difference between the bid price and the asking price when buying or selling a currency pair.
A narrow spread means that the trading cost is cheaper and a wide spread means that the trading cost is higher.
Take, for instance, USD/JPY is currently trading with an ask price of 0.6915 and a bid price of 0.6911, then the spread or the cost of trading USD/JPY will be the asking price (0.6915) minus the bid price (0.6911) in multiple of the trading lot size.
In an open long position, the market price must rise above the bid price (covering the cost) as the trade moves into profit. But in a short position, the market price must drop below the asking price (covering the cost of a short position) as the trade moves into profit.
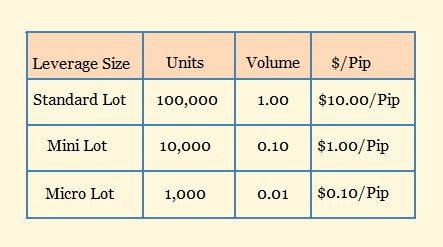
- Lot sizes in forex trading
Currencies are traded in specific amounts called lots which means the number of currency units that can be used to buy or sell in order to standardise forex trades.
Trading with an appropriate lot size that best balances opportunity and risk is a very important decision based on individual risk tolerance.
Micro lots are the smallest tradeable lot sizes provided by most brokers. Micro lots represent 1,000 units of an open trade. If you are trading a dollar-based pair, one pip would be equal to ten cents.
Mini lots represent 10,000 units of an open trade. One pip would equal 1 dollar trading a dollar-based pair
The standard lot represents 100,000 units of an open trade. Thus an opened trade will fluctuate by $10 for each pip move.
Image of lot sizes
- Leverage trading
Leveraging remains one of the most important aspects of risk management that must be taken seriously by traders of all levels (beginner, intermediate and professional traders) to ensure discipline, orderliness and longevity in the forex trading market.
Leverage simply means to take advantage of an opportunity in order to achieve a bigger goal or bigger objective.
The same theory applies to forex trading. Leverage in forex simply means to take advantage of a certain amount of capital provided by a broker so as to utilize more trading volume and maximize profit from relatively small changes in price movements.
- Margin in forex trading
Retail forex trading utilizes the leverage made available by a broker, to execute market orders and open trade positions that a retail account balance usually can't.
Margin comes into play as a portion of the trading account balance set aside to keep floating trades open and to ensure that potential losses are covered. It is required that a retail forex trader put up a specific sum of money (known as margin), a form of collateral required to keep leveraged positions running. The remaining uncollateralized balance that the trader has left is what is referred to as the available equity.
The margin level is therefore expressed as a percentage, calculated as the ratio of equity in the account to the used margin.
Click on the button below to Download our "What is forex trading and how does it work" Guide in PDF



